Heat and Temperature
Terms
Heat - energy transferred due to temperature difference
Heat transfer (
Temperature (
Internal Energy (also called thermal energy) (
Thermal Equilibrium
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: If object 1 is in thermal equilibrium with objects 2 and 3, respectively, then objects 2 and 3 must also be in thermal equilibrium. A system has reached equilibrium if net heat transfer over time is zero.
If
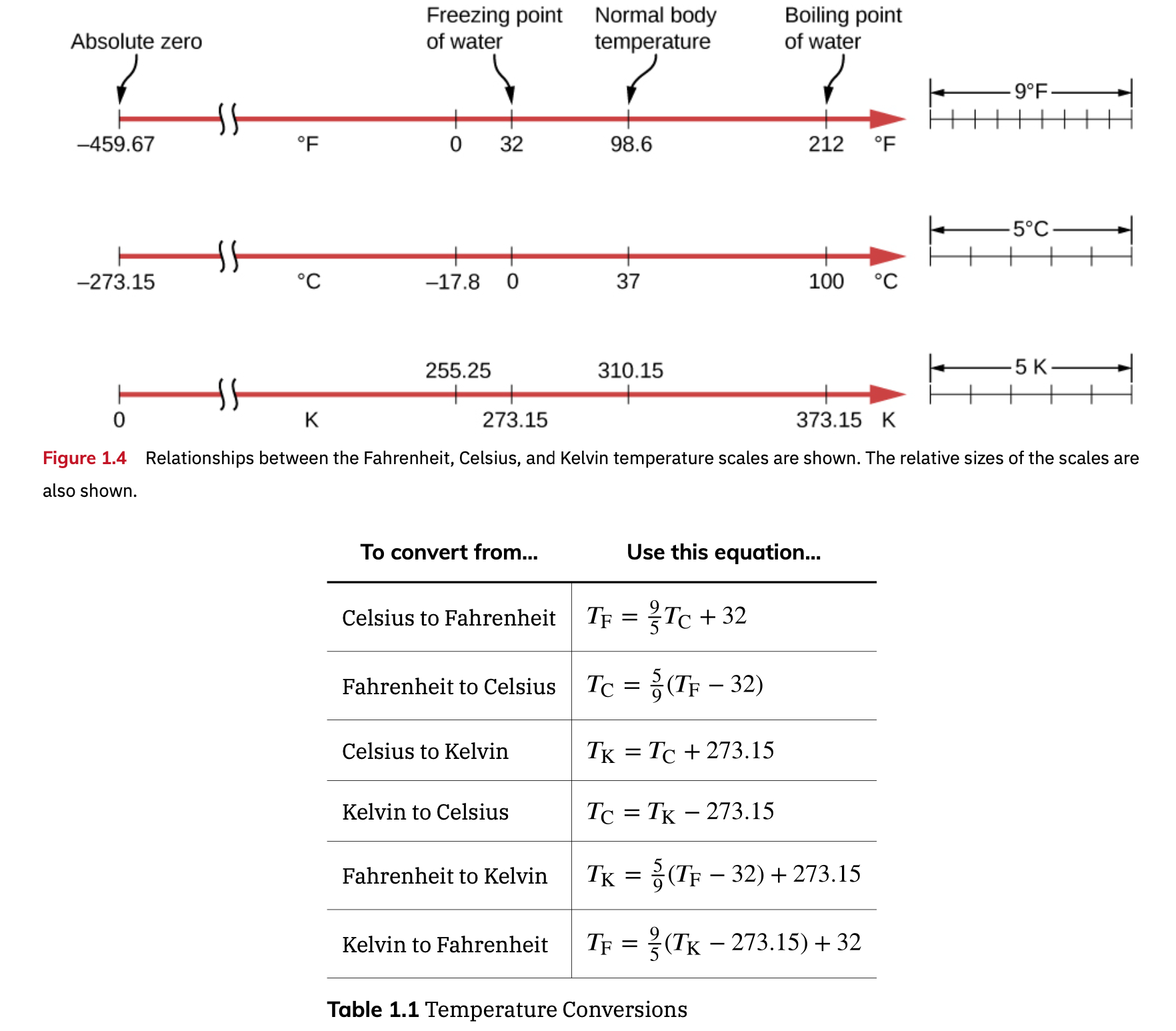
Different Temperature Scale (C, F, and K)
Linear Thermal Expansion
One Dimension
Note: for solid that is "isotropic", expand in all directions equally
We have an approximation equation for change in length,
Two Dimensions
Note: for small temperature change
The equation for thermal expansion for area approximation:
Three Dimensions
Note: need to use
Note: an approximation for small temperature change
Internal Energy, Heat, and Work
Internal energy is proportional to temperature
Work can also produce the same effect as heat transfer. Put differently, the
State variable and not state variable
Heat Capacity
Note: approximation of heat transfer due to temperature change
Phase Diagram
The phase of a substance depends on pressure (
Example: Phase Diagram or
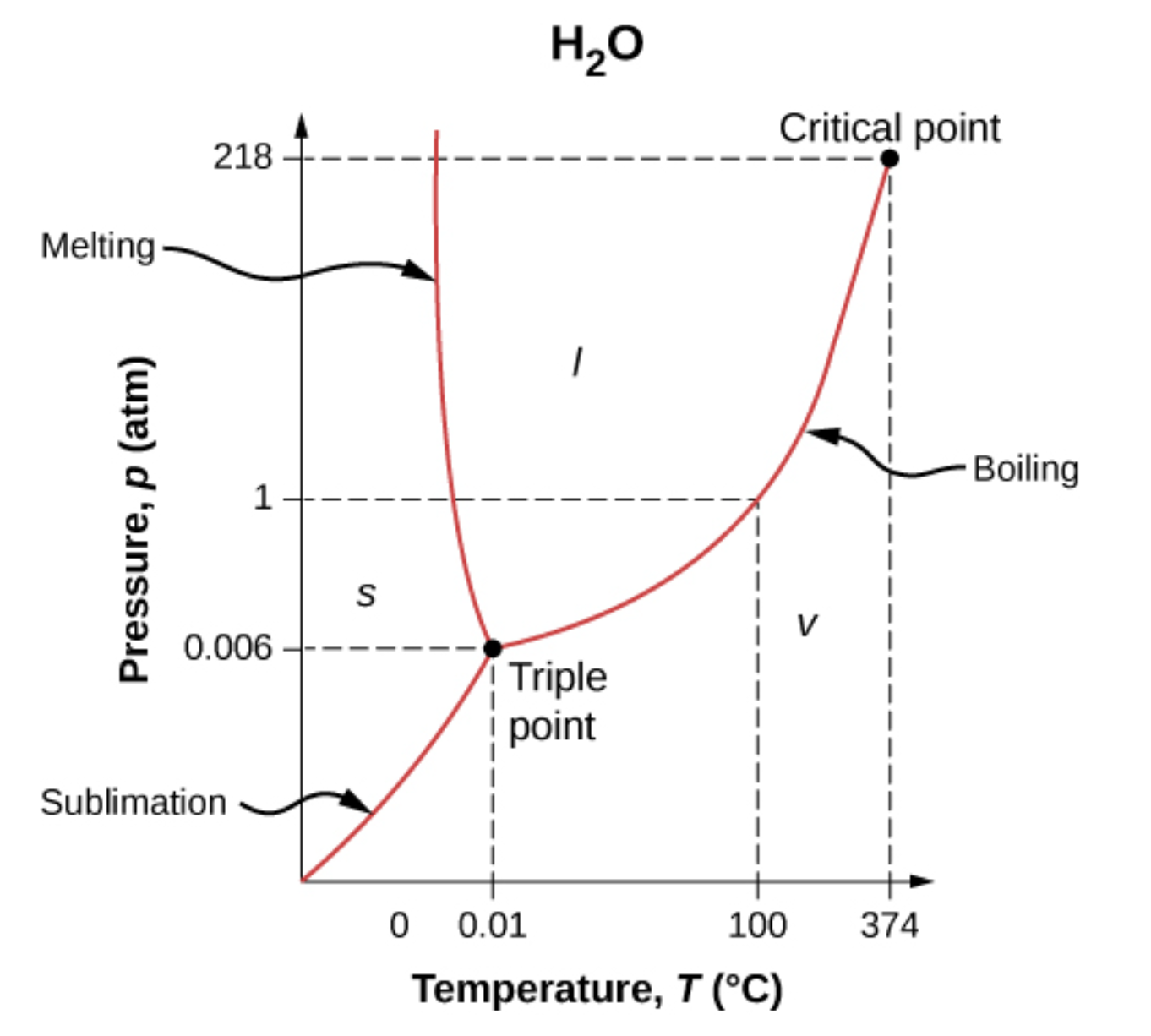
The phases of water for different pressure and temperature. It should show the solid (s), liquid (l) and vapor (v) regions.
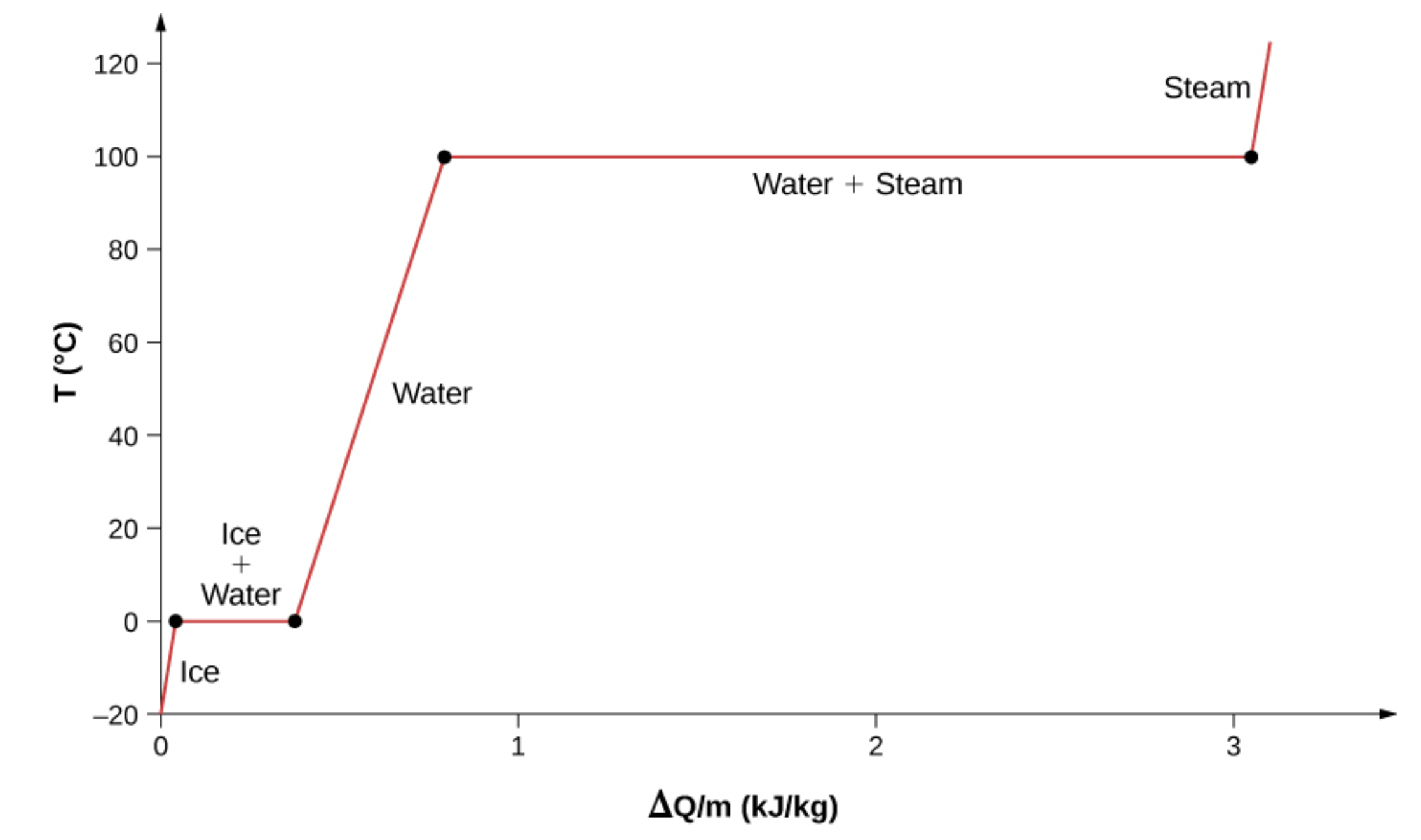
Latent Heat
Phase transition does not cause temperature change. This is called latent (Latin for hidden) heat.
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
Note: think of the mechanism
Conduction - transfer of heat by physical contact
Convection - transfer of heat by physical movement of a fluid (note: air is consider a fluid)
Radiation - transfer of heat by electromagnetic radiation
Conduction
Three conditions that affect conduction heat transfer: (1) thermal conductivity, (2) temperature difference, (3) area of contact & thickness (i.e., the distance between the hot and cold):
Convection
(Retyping)
Radiation
Rate of heat transfer by emitted radiation (also called Stefan-Boltzmann law of radiation):